The Anatomy Of An Effective ChatGPT Prompt
Updated May 27, 2024
Published May 30, 2023

Introduction
The way we shape our ChatGPT prompts can drastically influence the responses we receive, steering the AI toward the information we seek.
In this ChatGPT prompt guide, we’ll strip down to the essentials of prompt engineering, shedding light on the key aspects of a good prompt: Specificity, Clarity, Contextual Information, Tone, Style, and more. Whether you’re a seasoned AI enthusiast or a beginner setting foot in the AI domain, this guide aims to help you learn prompt engineering, and equip you with the understanding and tools to leverage the full potential of ChatGPT effectively.
Primary Components of a Good Prompt
Mastering the art of ChatGPT prompt crafting revolves around understanding and effectively applying three key components: Specificity and Clarity, Contextual Information, and Setting the Tone and Style. Let’s delve into each of these facets, uncovering their importance and illustrating their impact through concrete prompt engineering examples.
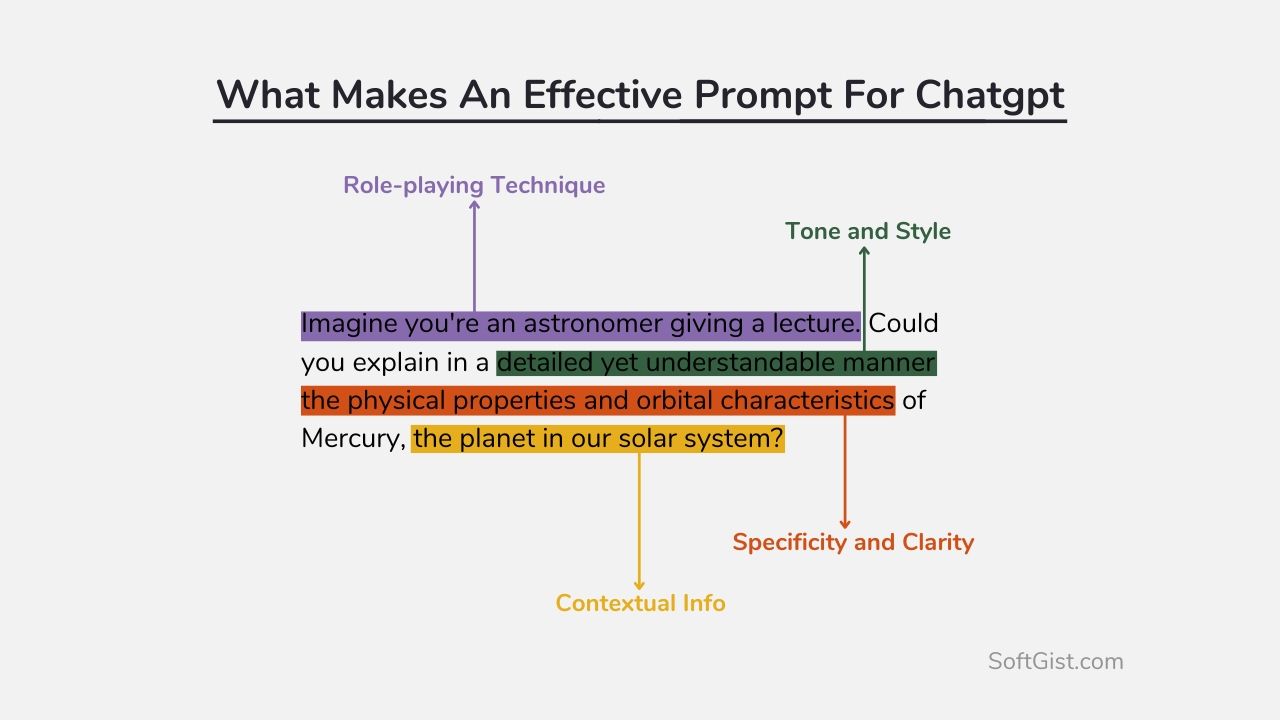
Example of what makes an effective prompt for ChatGPT
Specificity and Clarity
The first key to effective prompt engineering lies in being specific and clear. Consider your prompt as a roadmap you give ChatGPT to generate a response. The more specific and clear your instructions are, the better aligned the AI’s output will likely be with your desired result.
Take this example. If you prompt ChatGPT with, “Tell me about animals,” the resulting output could cover a vast range of topics from domestic pets to exotic jungle creatures, or from behavioral studies to conservation efforts. This kind of open-ended query can lead to an output that, while technically accurate, may not align with your intended focus.
However, refining the prompt to, “Can you provide detailed information on the habitat and lifestyle of African elephants?” pinpoints a specific area of interest. The more precise query sets a clear path for the AI to follow, yielding a more tailored and valuable response.
More examples:
Open-Ended: “Tell me a story.”
Specific and Clear: “Can you write a short fantasy story about a knight rescuing a dragon from a princess?”
Open-Ended: “What’s the weather like?”
Specific and Clear: “Can you provide the current weather conditions in Paris, France?”
Open-Ended: “Give me a recipe.”
Specific and Clear: “Can you share a recipe for a vegetarian lasagna that serves four people?”
Open-Ended: “Write about space.”
Specific and Clear: “Can you write a brief summary of the discovery and importance of black holes in the field of astronomy?”
Open-Ended: “Tell me about music.”
Specific and Clear: “Can you provide an overview of the evolution of classical music from the Baroque to the Romantic era?”
Open-Ended: “Teach me something.”
Specific and Clear: “Can you explain the basics of Python programming, specifically variables, loops, and functions?”
Contextual Information
Another crucial aspect of prompt engineering is providing enough contextual information. Context serves as a flashlight, illuminating the right path among many that the AI could potentially take.
Let’s illustrate this with an example. If you ask ChatGPT, “Can you tell me about Hamilton?” the AI has a broad spectrum of potential answers. It could generate a response about Alexander Hamilton, the Founding Father of the United States, the city of Hamilton in Ontario, Canada, or the globally popular Broadway musical ‘Hamilton.’
But if you modify the prompt to, “Can you provide a summary of the plot and main characters in the Broadway musical, ‘Hamilton’?” you give the AI essential context to focus its response accordingly. By doing so, you help the AI bypass irrelevant information and zero in on the exact topic you’re interested in.
Vague: “What’s the situation in Phoenix?”
Contextual: “Can you provide the latest COVID-19 statistics and guidelines in Phoenix, Arizona?”
Vague: “Tell me about Mercury.”
Contextual: “Can you explain the physical properties and orbital characteristics of Mercury, the planet in our solar system?”
Vague: “Write about Java.”
Contextual: “Can you write an introductory guide for beginners on Java programming language?”
Vague: “Discuss Apple.”
Contextual: “Can you provide an overview of Apple Inc’s impact on the smartphone industry since the introduction of the iPhone?”
Vague: “Give information about Paris.”
Contextual: “Can you provide a historical overview of Paris, focusing on its development from the Middle Ages to the present day?”
Vague: “Talk about Churchill.”
Contextual: “Can you summarize the major accomplishments and challenges of Winston Churchill’s tenure as British Prime Minister during World War II?”
Tone and Style
Interestingly, ChatGPT has a knack for picking up on the tone and style of a prompt, adjusting its output to mirror the mood you set. If you adopt a serious tone, you’ll likely receive a formal response. Opt for a casual approach, and the AI will likely reciprocate in kind.
Consider the following prompt: “Could you provide an analysis of the benefits and potential drawbacks of renewable energy sources?” In response to this formal, somewhat academic query, ChatGPT is likely to return a detailed, measured evaluation, similar in tone and style to the prompt.
Alternatively, if your question takes a more casual tone, such as, “Could you share some insights on solar power? Any potential pitfalls along with its benefits?”, you’re likely to receive a response that reflects the laid-back nature of your question.
By consciously setting the tone and style, you can guide ChatGPT towards generating a response that not only answers your question but also suits the audience and purpose of your inquiry.
Here are some examples that highlight how the Tone and Style of the prompt can shape ChatGPT’s response:
- Formal: “Could you elucidate the principle tenets of quantum mechanics, paying special attention to the Heisenberg uncertainty principle?”
Informal: “Hey, can you break down this quantum mechanics stuff? I’m really curious about this Heisenberg uncertainty thing.” - Professional: “Please provide a detailed summary of the 2023 fiscal policy changes in the European Union and their potential impact on small businesses.”
Casual: “Can you give me the lowdown on how the new 2023 money rules in the EU might hit small businesses?” - Academic: “Could you provide a comprehensive analysis of Shakespeare’s use of iambic pentameter in his sonnets?”
Colloquial: “Can you help me understand how Shakespeare used rhythm in his sonnets?” - Technical: “Please elaborate on the role of convolutional neural networks in the field of image recognition.”
Layman: “Can you explain in simple terms how computers learn to recognize pictures?” - Formal: “Please provide a detailed overview of the global efforts in renewable energy development.”
Informal: “What’s the worldwide scoop on creating green energy?”
By consciously choosing your tone and style when crafting the prompt, you can guide ChatGPT toward generating a response that suits the context, audience, and purpose of your inquiry, be it professional, academic, technical, or casual.
- Formal: Characterized by adherence to established forms or norms. Formal tone employs precise language and avoids using colloquialisms or slang. This tone is commonly used in academic or professional settings.
- Informal: Contrasts with the formal tone, using everyday language, colloquial expressions, and a more relaxed approach. It’s typically used in less official settings or when trying to foster a sense of familiarity or ease.
- Professional: A professional tone is respectful, direct, and unemotional. It often avoids personal pronouns and emotional language, focusing instead on clarity and effectiveness in communication.
- Casual: Casual tone is relaxed and uses simple language and phrases. It can include conversational language and might seem more personal or friendly.
- Academic: This tone is scholarly, intellectual, and authoritative. It often involves the use of industry-specific terms, citations, and a structured approach.
- Conversational: This tone mimics the natural flow of a friendly conversation. It’s generally warm, engaging, and inviting, using personal pronouns and questions to engage the reader.
- Persuasive: This tone aims to convince the reader or listener of a certain point of view. It employs various rhetorical devices, including emotional appeals, the use of strong evidence, and compelling language.
- Narrative: This style is used when telling a story or describing events in a way that the reader can imagine. It often involves using descriptive language and details to engage the reader’s imagination.
- Descriptive: This tone aims to paint a picture, allowing the reader to clearly visualize a person, place, thing, or idea. It uses vivid and sensory language to create detailed and engaging descriptions.
- Technical: This tone is used when discussing specific details about technology or complex processes. It’s precise, often includes industry jargon, and assumes a certain level of understanding from the reader.
- Enthusiastic: This tone conveys excitement and passion about the subject. It often uses exclamation points, powerful adjectives, and a lively, energetic style.
- Sincere: This tone is genuine and earnest, indicating the writer’s good intentions and honesty. It aims to build trust with the reader.
- Humorous: Characterized by jokes, puns, and funny anecdotes. A humorous tone can help engage the reader, making the content more memorable and enjoyable.
- Sarcastic: This tone is marked by irony or mockery, often used to express scorn or ridicule. It can add edgy humor to content but should be used carefully as it can be misunderstood.
- Witty: Characterized by humor and cleverness, a witty tone can be used to create engaging and enjoyable content. This tone can be great for livening up topics that might otherwise seem dull.
- Friendly: This tone is warm, inviting, and approachable. It aims to build a connection with the reader, often using a conversational style and personal pronouns.
- Passionate: This tone expresses strong emotions or beliefs about the subject matter. It can be compelling and persuasive, often evoking a strong response from the reader.
- Diplomatic: This tone is tactful and respectful, often used when handling sensitive issues or in negotiations. It seeks to find common ground, understanding, and positive outcomes.
- Assertive: This tone is confident and direct, expressing ideas or needs clearly and respectfully, without undermining the rights or beliefs of others.
- Colloquial: This tone uses informal language, idioms, and regional dialects, which can make content more relatable to specific audiences.
- Layman: This tone simplifies complex subjects to make them understandable for people without expert knowledge. It often avoids jargon and industry-specific language.
- Inquisitive: An inquisitive tone uses a lot of questions and expressions of curiosity. It can be great for exploring new ideas or subjects in an open-minded way.
- Analytical: This style is characterized by a logical and methodical approach to a subject. It tends to involve lots of evidence and a detailed examination of a topic.
- Expository: This style is used when the goal is to explain, inform, or describe. It’s typically fact-based, logical, and avoids personal bias.
The decision on which tone and style to use should ideally be driven by your intended audience and the objective of your dialogue. The most effective writers are those who can seamlessly adjust their writing’s tone and style to resonate with the specific audience and the situation at hand.
Role-Playing Technique
A particularly powerful strategy when crafting prompts for ChatGPT is the role-playing technique. This strategy is unique as it interacts dynamically with all three of the primary components of a good prompt: Specificity and Clarity, Contextual Information, and Tone and Style.
At its core, the role-playing technique involves assigning a specific role or persona to the AI and crafting your prompt in a way that enables the AI to embody that role in its response. By assigning a specific persona, you automatically enhance the specificity and clarity of your prompt. The assigned role (e.g., a historian, a scientist, a high school teacher) provides precise direction to the AI, indicating the kind of information you expect in the response.
Additionally, the role itself implicitly provides a level of contextual information. A historian, for instance, is expected to provide a historical context, a scientist would offer a scientific perspective, and a high school teacher would frame information in an educational context that’s suitable for high school students.
Finally, the persona dictates the tone and style of the response. A historian might use a formal and informative tone, a scientist could adopt a more technical style, and a high school teacher would likely use a clear and simple tone to explain concepts.
Let’s explore some examples of how the role-playing technique can be applied:
- As a science fiction author, describe a futuristic city.
- Pretend you’re a fitness coach, and advise on a workout routine for beginners.
- Imagine you’re a film critic. Review the latest James Bond movie.
- You’re a tour guide in Rome. Describe the must-visit sites for tourists.
- As an economist, explain the concept of inflation.
- You’re a motivational speaker. Provide tips on building self-confidence.
- Envision yourself as a children’s book author. Write a short story about a magical forest.
By consciously employing the role-playing technique in your prompts, you provide ChatGPT with clear directives and context, and set an expected tone and style for the response, thereby enhancing the overall quality and relevance of the AI’s output.
Prompt Case Studies
The real value in understanding prompt engineering becomes apparent when we can effectively apply these principles to generate useful AI responses. Let’s examine an pair of bad and good examples to better appreciate the importance of Specificity and Clarity, Contextual Information, and Setting the Tone and Style, as well as the use of the role-playing technique.
The Ineffective Prompt
Consider the following prompt: “Tell me about Mercury.” While it may seem acceptable at first glance, there’s a lot left to be desired in terms of specificity, context, and tone.
- Lack of Specificity and Clarity: This prompt is overly broad, leaving ChatGPT with an infinite number of potential paths to pursue. The resulting text might include topics ranging from the planet Mercury to the element mercury, or even the car brand Mercury. The lack of clear direction could lead to a response that feels scattered or irrelevant to your needs.
- Missing Contextual Information: Without additional context, ChatGPT cannot ascertain the exact focus of the prompt. Are we interested in Mercury’s role in astrology, its physical properties as a planet, or its use in thermometers? Without this guidepost, ChatGPT will generate a response based on its training data’s most common patterns, which might not align with your specific interest.
- Absence of Tone and Style: The prompt doesn’t convey any particular tone or style, making it difficult for ChatGPT to gauge whether to produce a formal, academic text, or a more conversational, casual piece.
The Improved Prompt
Now, let’s revise the prompt with our key principles in mind: “ChatGPT, imagine you’re an astronomer giving a lecture. Could you explain in a detailed yet understandable manner the physical properties and orbital characteristics of Mercury, the planet in our solar system?”
This revamped prompt addresses the shortcomings of the original in several ways:
- Enhanced Specificity and Clarity: We’re no longer just asking about “Mercury”. Instead, we’re asking for a “detailed yet understandable explanation” of the “physical properties and orbital characteristics of Mercury, the planet in our solar system.” This gives ChatGPT a clear and specific directive, increasing the likelihood of a suitable response.
- Added Contextual Information: The prompt now provides sufficient context, focusing the inquiry on Mercury as a planet in our solar system. This guides the AI in selecting the most relevant patterns from its training data, ensuring the response aligns with our specific topic.
- Set Tone and Style: By asking for an explanation in a “detailed yet understandable manner,” we’re signaling to ChatGPT that we want an informative, yet accessible response. This adjustment in tone helps tailor the AI’s output to a wider, non-technical audience.
- Incorporation of Role-Playing Technique: The prompt uses the role-playing technique by asking ChatGPT to imagine it’s an astronomer giving a lecture. This not only provides context but also helps to set the tone and style, as it implies a certain level of expertise and a specific way of communicating that information.
In short, the improved prompt incorporates Specificity and Clarity, provides ample Contextual Information, sets the Tone and Style, and uses the Role-Playing Technique, giving ChatGPT a detailed roadmap to generating the precise and pertinent information we’re seeking. The result of the new response is more likely to meet our needs and expectations, demonstrating the real-world value of proficient prompt engineering.
Other Considerations in Prompt Crafting
While the elements of Specificity and Clarity, Contextual Information, and Setting the Tone and Style are certainly crucial in prompt engineering, other considerations add nuance and depth to this practice. Let’s take a look at some other prompt engineering techniques – how the length of the prompt, ambiguity, cultural and temporal context, and managing expectations play into crafting effective prompts.
Length of the prompt
When it comes to prompt length, a “Goldilocks Principle” applies – not too short, not too long, but just right. A prompt that’s too brief may lack necessary context or clarity, while an overly verbose prompt might confuse the AI, leading to scattered or irrelevant responses.
For instance, “Talk about dogs” is too brief. It’s lacking in context, clarity, and specificity. At the other extreme, a lengthy prompt like “Can you provide a thorough analysis of the influence of dog breeding over centuries, detailing changes in breed characteristics, societal preferences, and ethical considerations, while comparing different countries?” could potentially overwhelm the model.
Instead, a prompt like “Can you explain how dog breeding practices have evolved in the last century in the United States?” strikes a balance – it’s clear, specific, and concise, providing enough information for the model without overloading it.
Handling Ambiguity
While clarity is usually key in prompt engineering, there can be situations where ambiguity works to your advantage. If you’re looking for a variety of ideas or creative inspiration, an intentionally ambiguous prompt might give you a wide range of responses. A prompt like “Generate story ideas involving a dragon and a castle” could result in a diverse array of interesting narratives.
However, in most cases, especially when seeking specific information or analysis, ambiguity can lead to vague or irrelevant responses. Understanding when to use ambiguity is a crucial skill in prompt crafting.
Cultural and Temporal Context
Sometimes, prompts may require additional cultural or temporal context to ensure an appropriate response. Consider asking for a summary of “the last season’s football results.” Without specifying which type of football (American, association (soccer), Australian, etc.) and which league or year, the model may provide irrelevant or unexpected results.
A more effective prompt would be “Can you provide a summary of the English Premier League’s football results from the 2022-2023 season?” This prompt includes cultural (English Premier League) and temporal (2022-2023 season) context, steering the model toward a more relevant response.
Managing Expectations
Finally, it’s important to understand and manage expectations when interacting with AI. Despite ChatGPT’s impressive ability to generate human-like text, it doesn’t truly “understand” information or possess consciousness. It uses patterns in its training data to predict responses but lacks the ability to reason, think critically, or make judgments.
For example, asking ChatGPT for its “opinion on the latest Marvel movie” might generate a response, but it won’t be based on the model’s personal experience or sentiment—it simply can’t watch or form an opinion on movies. It’s vital to recognize the model’s limitations and craft prompts accordingly.
Conclusion
Unlocking the full potential of AI models like ChatGPT boils down to the art of crafting effective prompts. We’ve journeyed through key aspects of this art, from the power of specificity and clarity to the nuances of contextual information and setting the right tone. We’ve also touched on balancing prompt length, harnessing ambiguity, and the importance of both cultural and temporal context.
But the understanding of these principles is only the beginning. Your journey with AI is a continuous exploration, and the key to success lies in trial and experimentation. If you wish to learn more advanced prompt engineering techniques, please check out our Ultimate Guide to Prompt Engineering.
Share This Post
Ada Rivers
Ada Rivers is a senior writer and marketer with a Master’s in Global Marketing. She enjoys helping businesses reach their audience. In her free time, she likes hiking, cooking, and practicing yoga.
Allow cookies
This website uses cookies to enhance the user experience and for essential analytics purposes. By continuing to use the site, you agree to our use of cookies.
